
HIV is a virus that attacks the immune system, which is our body’s natural defence against illness. The virus destroys a type of white blood cell in the immune system called a T-helper cell and make copies of itself inside these cells. While the government is taking adequate steps to safeguard the rights of HIV and AIDS patients, an important bill was passed in Rajya Sabha on 21st March 2016 to ensure equal rights to people who have HIV and AIDS in getting treatment, admission in educational institutions and jobs.
AIDS IS CAUSED BY HIV

AIDS is caused by HIV, the human immunodeficiency virus, which damages the body's defense system. People who have AIDS become weaker because their bodies lose the ability to fight all illnesses. There is no cure for HIV, but treatment is available to reduce the symptoms so that even people with the virus can have healthy, productive lives.
A PERSON MAY HAVE HIV AND NOT AIDS
HIV can be controlled if detected early and may not progress to AIDS at all. Moreover, it can take almost ten years for the onset of AIDS which is the most severe stage of this disease.
HIV IS A MANAGEABLE CONDITION
It requires certain lifestyle changes and regular medication, but HIV can be managed and controlled.
IT ATTACKS YOUR IMMUNE SYSTEM
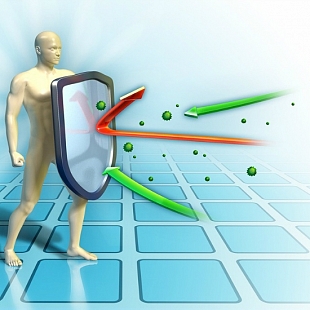
The HIV attacks your immune system thus making your more susceptible to infections and certain types of cancers.
HIV IS NOT TRANSMITTED BY EVERYDAY CONTACT

HIV is not transmitted by hugging, shaking hands, using swimming pools, toilet seats, sharing bed linens, eating food, mosquito and other insect bites coughing, sneezing.
IT IS TRANSMITTED BY SOME TYPES OF BODILY FLUIDS
HIV or AIDS can be transmitted through certain bodily fluids like blood, semen, breast milk and vaginal secretions but not sweat, urine or saliva.
PEOPLE WHO HAVE SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS ARE AT GREATER RISK OF BEING INFECTED WITH HIV.

People who have STIs are at greater risk of being infected with HIV and of transmitting their infection to others. People with STIs should seek prompt treatment and avoid sexual intercourse or practice safer sex.





